Vitamins are food substances found only in things that grow, such as animals and plants. They are essential for our bodies to function properly. The human body cannot make vitamins. They must be ingested either as dietary supplements or better yet in food. Vitamins cannot replace food–they must be used in conjunction with food.
However, even if you eat a healthy diet, there is no guarantee that you will properly digest and absorb your foods and nutrients, which is why you must also have adequate gastrointestinal function if you want to absorb your vitamins. I recommend investigating your gastrointestinal function annually, by doing a GI Map Stool test, regardless if you have gastrointestinal symptoms or not. Riboflavin is also given intravenously in our Vital Health Drips IV Therapy.
It is crucial to have adequate gastrointestinal function, as I mentioned above, so that all of our vitamins and minerals can be absorbed and enter into the Krebs Cycle, which allows us to make energy (ATP). Often if even one nutrient is missing, energy production comes to a halt. You can see in the image below, where each nutrient is needed in the process and where it enters the cycle.
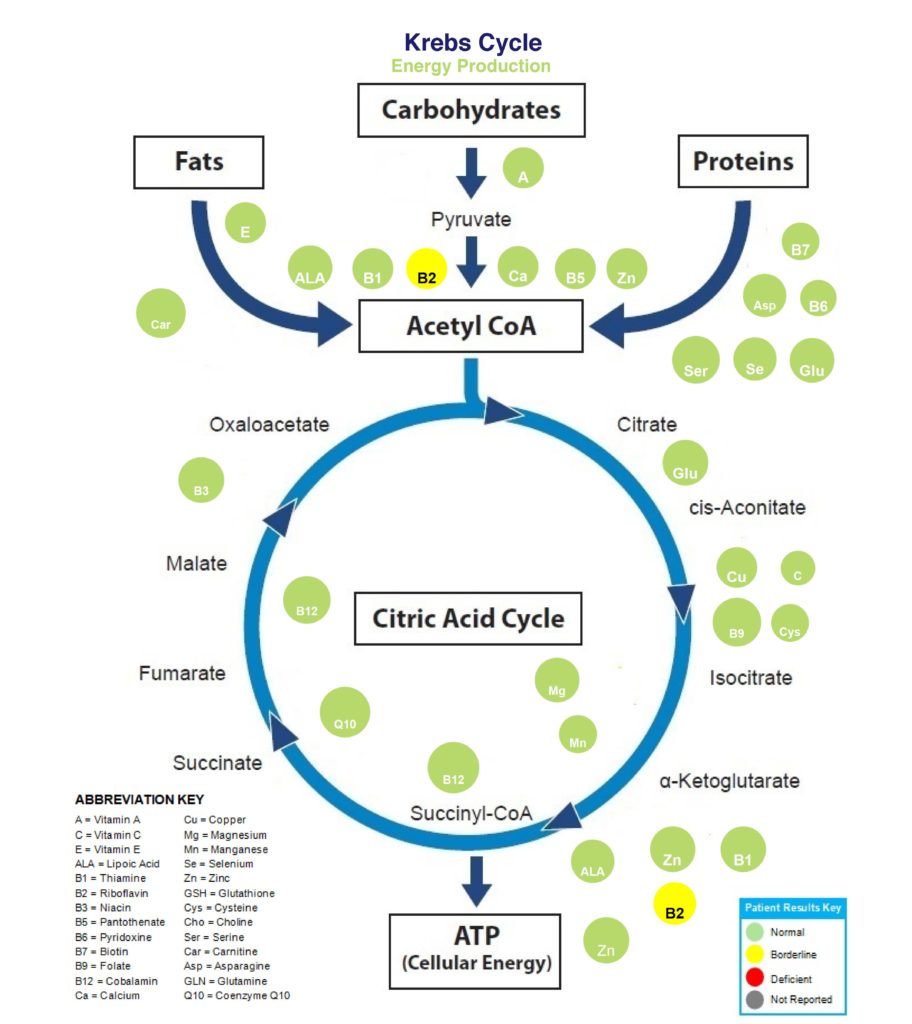
Likewise, our vitamins and minerals must also enter the methylation cycle, for control of detoxification, cellular adaptability, and gene regulation. Thus, so many body processes are dependent on adequate intake, digestion and absorption of our nutrients. Below is a depiction of the methylation cycle.
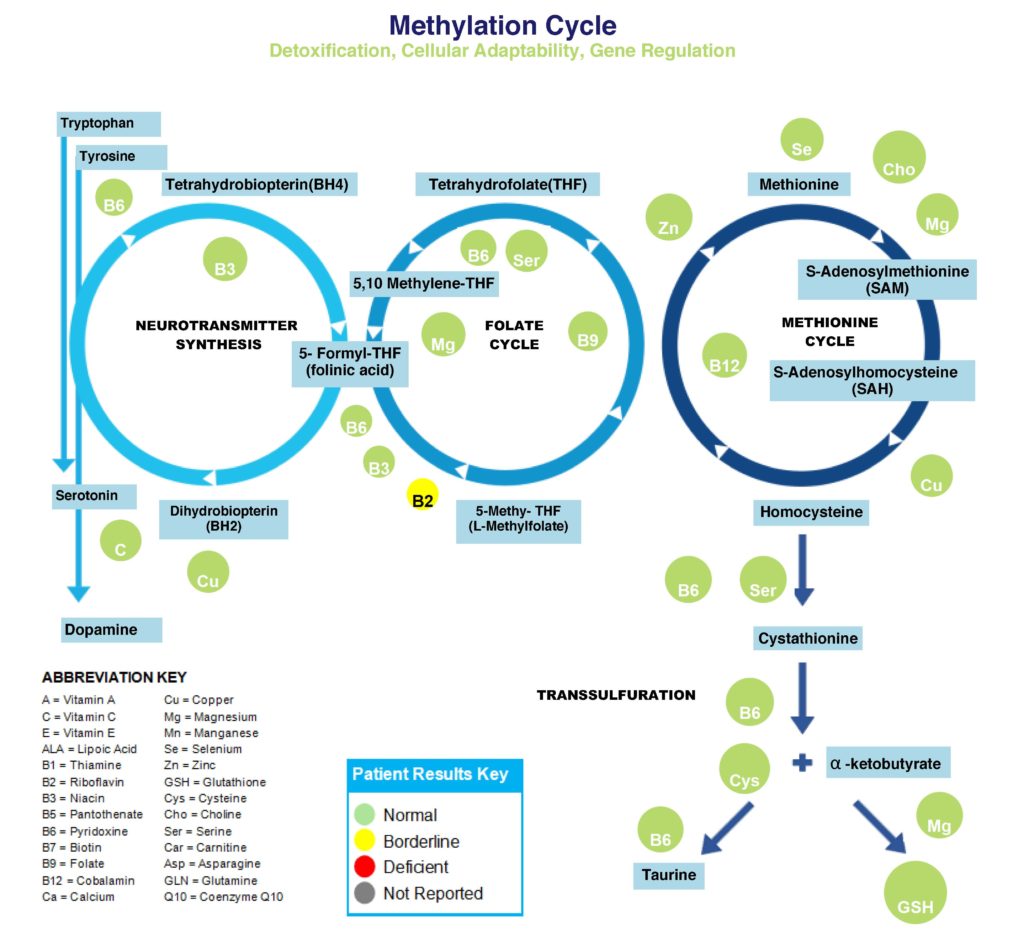
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is a component of enzymes involved in antioxidant function, energy production, detoxificaton, methionine metabolism and vitamin activation. It is a crucial B vitamin required for a significant amount of metabolic processes.
A COMMON DEFICIENCY PROFILE:
- migraine headaches
- anemia (iron)
- cheilosis
- chronic alcoholism
- oxidative stress
- mitochondrial dysfunction
- low uric acid
- oral and throat inflammation
Research proves that nutrients work synergistically so that the status of one nutrient typically impacts the status of other nutrients. Every vitamin and mineral should be evaluated within the context of other nutrients.
MONITOR THESE OTHER NUTRIENTS WHEN EVALUATING RIBOFLAVIN:
- glutathione
- homocysteine
Synergistic Nutrients:
- vitamin B3 (niacin)
- vitamin B6 (pyrodoxine)
Antagonistic Nutrients:
- Calcium: might form a chelate with riboflavin, decreasing its absorption
NUTRIENT-DRUG INTERACTIONS:
- oral contraceptives
- tricyclic antidepressants
- quinine
- adriamycin
- anti-psychotic medications
FOOD SOURCES OF RIBOFLAVIN:
- dairy: milk, cheese, eggs
- whole grains
- beef, chicken
- wheat germ
- fish
- broccoli
- asparagus
- spinach
- mushrooms
- almonds
ROLE IN DISEASES & METABOLIC DYSFUNCTION:
Hypertension:
- people with a certain gene (MTHR type TT) tend to respond well to vitamin B2 therapy for lowering blood pressure
Diabetes:
- needed to make glutathione that is needed to protect the body against free radical damage caused by elevated blood sugars
- people with diabetes often have poor riboflavin metabolism
- riboflavin 5-phosphate is the form desired and most supplments don’t use this form
Depression, Anxiety & Sleep:
- low levels implicated in depression due to its role in methylation reactions in the brain
Methylation:
- helps recycle folate into a usable methyl-donor form
- precursor for FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) which assists methylation reactions
Inflammation:
- helps minimize pain associated with inflammation
- detoxifies homocysteine, an amino acid that indirectly causes inflammation in various tissues







